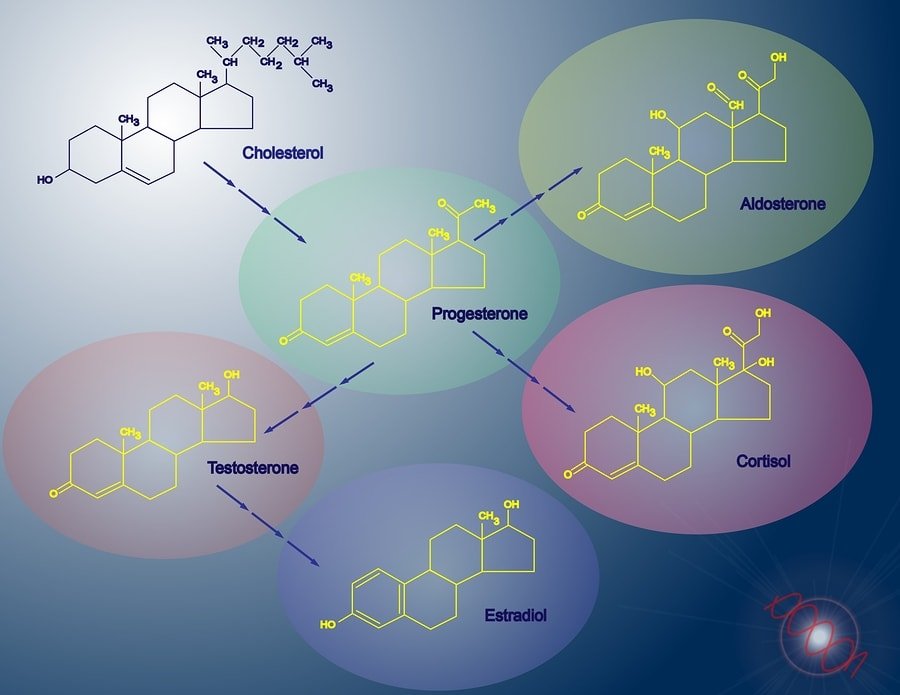
CYP11A1 is necessary for the production of steroid hormones, such as estrogen, testosterone, aldosterone, and cortisol. It converts cholesterol into pregnenolone, a precursor of all other steroid hormones. This enzyme also acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. However, it may increase susceptibility to allergies. Read on to learn more about CYP11A1 function, gene variants and factors that increase or decrease its activity.
What is CYP11A1?
This enzyme is also called the cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme or P450scc.
It is one of the cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (CYPs) [1]. CYPs eliminate toxins and drugs from the human body. However, some like CYP11A1, are not involved in detoxification but in steroid hormone production.
Read more about various CYPs here.
Function
This enzyme is a key enzyme in steroid hormone production. It converts cholesterol to pregnenolone – from which all other hormones are derived [2, 3, 4, 5].
It also processes vitamins D2 and D3 [3, 6].
The activity of this enzyme is age and sex-dependent [7].
Location
This enzyme is abundant in the adrenal gland, testis, ovary, and placenta [8, 9].
However, it is also active in the brain, skin, lungs, gut, bone, breast, and prostate [10].
Furthermore, it plays a function in the thymus and immune cells [10].
The Good
This enzyme is involved in steroid hormone production. It is necessary for testis development, pregnancy-related processes, and mating-related behavior [11].
In addition, CYP11A1 products act as anti-inflammatory agents. They decrease Th1/Th17 cytokines and NF-κB, while increasing IL-10 [10, 12].
Finally, there is evidence that CYP11A1 products have anti-cancer activity [10, 12].
Some of them show strong anti-tumor activity against breast cancer, liver cancer, glioma (brain cancer), and leukemia [10].
The Bad
This enzyme has a pro-allergic role. It favors the development of asthma and peanut-induced allergy in mice [13, 14, 15].
This is because steroid hormone production is an essential part of the Th2 response [15].
Decreasing the enzyme prevents allergic diarrhea and inflammation in mice [15].
Gene Polymorphism
People with partial or complete enzyme deficiency have adrenal insufficiency [2]. This is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones.
They also have sexual development disorders [2].
Lifelong hormone replacement therapy is necessary for this condition. Without therapy the disease is lethal [16].
The condition is rare. So far, only 19 patients with CYP11A1 complete deficiency-causing mutations have been reported worldwide [17].
RS2279357
rs2279357 was associated with autism spectrum disorder (100 families) [18].
Women with rs2279357 T/T are more prone to develop breast cancer (530 patients and 546 controls) [19].
RS11632698
rs11632698 was associated with aromatase-inhibitor-related bone loss (391 breast cancer patients) [20].
(TTTTA)n variant
A five nucleotide repeat variant in CYP11A1, when repeated four times (TTTTA)4, increases the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) (meta-analysis, 1,236 patients, and 1,306 controls) [21].
On the other hand, having a (TTTTA)6 variant, with 6 repeats, decreases the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) (meta-analysis, 1,236 patients, and 1,306 controls) [21].
People with (TTTTA)6 may have an increased risk of metastatic and high-grade prostate cancer (206 subjects) [22].
Increasing or Decreasing CYP11A1
These increase CYP11A1
- Ginseng (Panax ginseng) [11]
- UVB and UVC [10]
- Bisphenol A (BPA) [23]
- Pemirolast, clobenpropit, desogestrel, dexmedetomidine, and tizanidine [24]
These decrease CYP11A1:
- Ketoconazole, posaconazole, carbenoxolone, and selegiline [24]
