Melatonin plays many important roles in the immune system and inflammation control. Scientists have observed abnormalities in melatonin function in a range of autoimmune conditions. Read on to learn more about the effects of melatonin on immunity and inflammation and discover the potential side effects of supplementation.
Melatonin Reduces Inflammation and Supports Immunity
Please note: the beneficial roles of melatonin as a naturally occurring hormone may not imply the same benefits of melatonin supplementation.
Melatonin receptors are present in a wide variety of immune cells [1].
Melatonin is immunomodulatory, which means that it reduces excessive immune function in inflammatory conditions and enhances immune function in immunocompromised people.
Source: http://www.jpp.krakow.pl/journal/archive/12_07_s6/pdf/115_12_07_s6_article.pdf
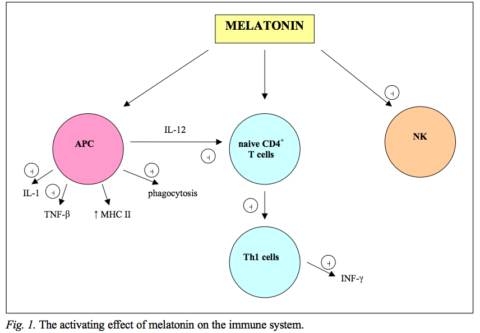
Melatonin plays an important role in the immune system. The membranes of immune cells such as CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and B cells all have melatonin receptors [2].
Melatonin can either activate or suppress immune cells [2].
In mice, melatonin treatment increased the production of T cells, natural killer cells, and monocytes. The nuclear melatonin receptor also induces cytokine production [2].
Relationship with Th1/Th2/Th17 Cells
Melatonin is involved in Th1/Th2 development. The balance of T helper 1 and T helper 2 cells plays a critical role in controlling cellular immune responses [3].
Th1 cells play a key role in the development of inflammatory responses. They help with the production of proinflammatory cytokines like IFN-y and IL-2 [1].
On the other hand, Th2 is anti-inflammatory. Th2 cells produce cytokines like IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 and IL-13 [1].
Depending on its concentration, melatonin promotes both Th1 and Th2 responses. In mice, low doses of melatonin increased Th1 cytokine levels. In contrast, high doses decreased the pro-inflammatory cytokines [1, 3].
Melatonin suppresses the development of Th17 cells and increases regulatory T cells [4].
Suppresses Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
According to preliminary research, melatonin blocks the release of the following cytokines and inflammatory substances:
- TNF-alpha from macrophages in response to LPS (lipopolysaccharides) [5]
- Nitric oxide (which causes oxidative stress) from immune cells in response to LPS [6]
- iNOS, COX-2, and MMPs (by blocking NF-κB) [2]
- IL-1β and IL-6 [2]
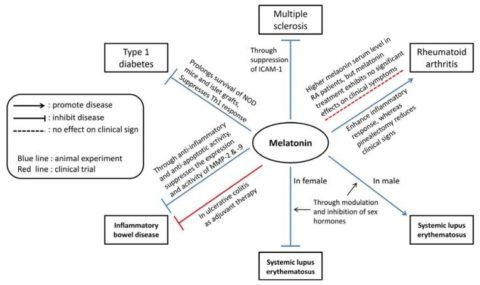
Melatonin and Autoimmune Diseases
Connection Between Melatonin and the Immune System
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3709754/figure/f1-ijms-14-11742/
1) Type 1 Diabetes
Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing β cells in the pancreas causes Type 1 diabetes (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus). Pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IFN-γ contribute to β cell destruction [2].
In non-obese diabetic mice (an animal model of type 1 diabetes), chronic administration of melatonin increased survival and delayed the onset of diabetes [7].
Type 1 diabetes is a Th1-cell-dominant disease, while melatonin shifts the immune response toward Th2 cells [2].
By reducing TNF-α and IFN-γ production, melatonin may protect against β cell destruction [2].
Surgical transplantation of pancreatic islet grafts (cluster of cells) that produce insulin is a potential therapy for type 1 diabetes. However, the immune system might attack or reject the transplants. Melatonin might be able to prolong graft survival [2].
In diabetic mice, melatonin administration decreased Th1 cells and increased anti-inflammatory IL-1o cytokines. This inhibits the autoimmune response to the islet transplants. On average, the islet grafts survived for 17 days with melatonin treatment in comparison to 7 days in untreated mice [8].
2) Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease that affects the central nervous system. Immune cells wrongly attack the neurons’ myelin sheaths. This causes pain, fatigue, weaknesses, and may even cause vision loss [2].
Multiple sclerosis patients excrete an abnormal amount of melatonin metabolites in the urine at night. This indicates a dysregulation of melatonin production [2].
Melatonin deficiency plays an important role in the fluctuation of multiple sclerosis symptoms, fatigue, and mood disorders in patients [9].
Th17 cells also contribute to multiple sclerosis. Melatonin suppresses Th17 cells, which may help stop the progression of the disease [10].
In rats with MS, oral melatonin administration significantly reduced paralysis severity. These effects were due to the suppression of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 production in the spinal cord [11].
However, there were conflicting results from a different study. Luzindole is a melatonin receptor blocker, which means that it inhibits melatonin receptor activity. Luzindole-treated mice did not develop EAE, while control mice did [12].
3) Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are referred to as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Characteristics of IBD include the accumulation of immune cells in the intestinal tissues and inflammation in the intestines [2].
The immune cells that accumulate in the intestinal tissues include B cells, T cells, neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Activation of these cells causes inflammation and increases proinflammatory cytokine levels [2].
Melatonin might protect against IBD by reducing pro-inflammatory markers (TNF-a and NF-κB), DNA damage, and oxidative stress [2].
Short-term melatonin administration reduces inflammation in a mouse model of colitis [13].
However, the same study found that long-term administration of melatonin worsened colitis symptoms and caused intestinal cell death in mice [13].
Various case studies also showed conflicting effects of melatonin in humans. While daily melatonin supplementation helped one patient reduce colitis symptoms, it worsened IBD symptoms in two others [14].
In a study of 60 ulcerative colitis patients, melatonin reduced intestinal inflammation when added to standard treatment. It also helped the patients sustain remission (disease symptoms became less severe) [15].
4) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Melatonin administration may help treat animal models of lupus. However, its effects may depend on the timing of administration and the gender of the subject [1, 16].
Daily melatonin injections enhanced survival rates in female mice in the morning. However, evening treatments did not change survival rates [17].
One month of melatonin administration in female rats decreased inflammatory cytokine production. It also increased the induction of anti-inflammatory IL-10 production [18].
However, in the same study, melatonin treatment worsened lupus symptoms in male mice. It increased inflammatory cytokines and autoantibodies [18].
When melatonin reduces testosterone, it increases pro-inflammatory cytokines. This might be the cause of melatonin’s negative effects in male mice [19].
5) Rheumatoid Arthritis
Melatonin tends to promote the development and increase the severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis patients have increased melatonin concentration in their blood [20].
In one study, 75 patients either received 10 mg of melatonin (considered a high dose) at night or a placebo for six months. Melatonin increased ESR and neopterin, which are indicators of inflammation [21].
However, there was no significant difference in rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and proinflammatory cytokine levels in melatonin and control groups [21].
In one study, researchers surgically removed the pineal gland, which produces melatonin, in mice with RA. These mice had significantly reduced levels of IL-1β and IL-6 in their blood and brains, which indicated lower inflammation [22].
In a similar study, the mice showed reduced severity of arthritis, suggesting that melatonin worsens disease severity [23].
Melatonin Side Effects & Precautions
Melatonin supplements are generally safe and well-tolerated. Oral supplementation of melatonin at 240 mg and injections at 500 mg are possibly safe for healthy individuals [24, 25].
Potential side effects include [26, 27]:
- Headaches
- Insomnia
- Rash
- Upset stomach
- Low blood pressure
- Nightmares
The most important thing to remember about melatonin supplementation is the timing. Inappropriate timing of melatonin administration can cause hormonal problems, daytime sleepiness, and desensitization of melatonin receptors [27].
Administration throughout the day may also contribute to bipolar disorder and depression symptoms [26].
Additionally, melatonin activators (like Ramelteon or Agomelatine) should not be used in patients with liver failure, kidney failure, alcohol addiction, or high fat levels [28].
Melatonin and bright light are known to improve the mood and symptoms of Alzheimer’s patients. However, without the additional bright light, it may have a negative effect on the mood of such patients. It may also lead to an increase in aggressive behavior [29].
Drug Interactions
Supplement-drug interactions can be dangerous and, in rare cases, even life-threatening. Always consult your doctor before supplementing and let them know about all drugs and supplements you are using or considering.
Due to potential drug interactions, caution and medical supervision are warranted before combining melatonin with [30, 31, 32, 33, 34]:
- Blood thinners
- Anticonvulsants (drugs for seizures)
- Antidiabetic drugs
- Sedative drugs
- Psychostimulants
- Blood pressure-lowering drugs
- Immunosuppressants