AMPK is an energy sensor that, when activated in certain tissues, has many beneficial effects on our bodies. It stimulates the metabolism, improves insulin sensitivity, decreases inflammation, and improves muscle performance. AMPK is also involved in several longevity pathways and may promote healthy aging.
AMPK: The Energy Enzyme
AMPK (5′ AMP-activated protein kinase) is an enzyme that plays a key role in energy balance. All creatures from yeast to humans have this enzyme [1].
AMPK can detect the level of energy (number of ATP molecules) in a cell and helps regulate responses when it gets too low or high.
AMPK is produced in a number of tissues, including the liver, brain, fat cells and muscle [1].
While much of AMPK activity is dependent on external factors such as diet and exercise we all have a genetic disposition inherited from our parents.
Health Effects of AMPK Activation
1) Increases Metabolism
AMPK in the hypothalamus senses our level of energy production in the body (in the form of ATP). It increases energy expenditure and can also increase appetite (when it is activated in the hypothalamus) [2].
When cellular energy is low, AMPK is activated and targets a range of processes, the net response of which is an increase in energy production and a coordinated decrease in energy (ATP) usage [3].
Hypothalamic AMPK increases appetite, increases glucose production and uptake, reduces heat production, and decreases energy output [2].
2) Produces and Burns Sugars
Glucose is the main source of energy for the body and is particularly essential for normal brain activity. Hypoglycemia, a condition in which the blood glucose drops below normal levels, poses a great danger to the stability and functioning of the brain and therefore activates AMPK [2].
Hypothalamic AMPK activation promotes glucose production from the liver [2] and glucose uptake into the muscles [4].
AMPK inhibits glucose storage (glycogen synthesis), resulting in more glucose being available for energy production [4].
In various cells, AMPK stimulates the breakdown of glucose for energy (in the form of ATP) [4].
3) Burns Fat
AMPK inhibits the production of fatty acids, cholesterol, and triglycerides, and instead stimulates the breakdown and burning of existing fat for energy [4].
4) Inhibits Protein Production
Protein production is a high-energy process that is inhibited during low energy states to conserve energy. Therefore, it is not surprising that AMPK inhibits protein production [4].
Inhibiting excessive protein production results in a much more energy-efficient and less wasteful cell.
5) Promotes Cellular Recycling (Autophagy)
Autophagy is the process of recycling cellular components. This process promotes molecular and cell subunit quality control by degrading damaged or misfolded proteins and even damaged mitochondria [3].
Autophagy can contribute to energy generation by providing fuel for mitochondrial metabolism, and AMPK promotes this process [4].
6) Regulates the Mitochondria
AMPK is capable of both acute and long-term improvement of mitochondrial activity [3].
AMPK also regulates the production and turnover of mitochondria. Loss of AMPK in mice reduces mitochondrial activity and greatly diminishes muscle performance [3].
7) Acts as an Antioxidant
AMPK has a crucial role in increasing antioxidant defense during oxidative stress [4].
AMPK increases the production of several antioxidant proteins, such as NRF2, superoxide dismutase and uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) [4].
8) Helps With Oxygen Delivery
Upon hypoxia (low oxygen) at altitude or during sleep, activation of AMPK may protect against acute breathing instability. Loss of AMPK was shown to cause breathing dysfunction during hypoxia in mice [5].
Variations of gene components of AMPK has been found in high-altitude Andean populations, presumably in order to improve survival in low oxygen conditions [5, 6].
9) Important for Fertility
In several animal species, AMPK increases the production of sex hormones [7].
The absence of AMPK leads to reduced fertility in both sexes [7].
10) Increases Blood Flow
AMPK plays a critical role in increasing blood flow through vasodilation (widening of the blood vessels), by stimulating nitric oxide release in blood vessels [8].
11) May Promote Healthy Weight
AMPK outside of the brain increases fat burning, and this pathway can result in weight loss [9].
By contrast, AMPK activation in the brain increases appetite. In mice, when the activity of brain/hypothalamic AMPK was inhibited, the mice ate less and lost weight. When AMPK activity was raised the mice ate more and gained weight [10].
Ghrelin, the hunger hormone, stimulates AMPK in the hypothalamus [11].
12) May Promote Longevity
AMPK activation gradually declines during aging. Some researchers believe that the age-related increase in chronic inflammation levels is responsible for the suppression of AMPK activity [4].
Activating AMPK may help multiple longevity pathways and promote healthy aging [3].
Many studies have shown that AMPK plays a crucial role in increasing longevity and calorie restriction-induced lifespan extension in worms, fruit flies, and rodents [4].
In worms, AMPK activation can increase lifespan by as much as 15% [12].
AMPK increases longevity by reducing protein production [3] and enhancing autophagy [3].
Longevity Pathways of AMPK
- AMPK activates longevity FOXO proteins [3]
- AMPK activates the master antioxidant regulator NRF2 [4]
- AMPK inhibits the ‘master regulator’ of lipogenesis SREBPc [3]
- AMPK inhibits mTOR indirectly [3]
Longevity research is a contentious and controversial field, and the precise role of AMPK in determining lifespan is unknown. Much more research is required to determine this enzyme’s role in aging and longevity.
14) Helps Decrease Inflammation
AMPK can both decrease inflammation and be decreased by inflammation.
AMPK also exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects. AMPK inhibits inflammation by indirectly inhibiting NFκB, a key activator of inflammation [4].
While AMPK could have many beneficial effects in chronic inflammation, it is typically reduced in such states.
15) Improves Diabetes
AMPK activation improves insulin sensitivity [4].
AMPK deficient mice showed impaired glucose tolerance [13].
Metformin, an activator of AMPK, is the most frequently prescribed antidiabetic drug for type-2 diabetic patients [4].
16) Benefits the Heart
The activation of AMPK also performs a protective role in cardiovascular diseases [14].
17) Increases Testosterone
AMPK can increase male hormones/androgens in human cells [15]. However, metformin (AMPK activator) is commonly given to women with PCOS to a good effect (PCOS is a condition with higher male hormones); much more research is required to determine AMPK’s role in testosterone production.
A Role in Neurodegenerative Disease?
AMPK has both protective and contributing properties when it comes to neurodegenerative diseases, and studies often come to opposing conclusions regarding this enzyme and its role.
In mice with Alzheimer’s, activation of AMPK by metformin was shown to increase amyloid-beta protein (Aβ) levels and therefore contribute to the disease [3].
However, Aβ generation was also shown to be increased in AMPK deficient mice [13]. Furthermore, AMPK activation by resveratrol and AICAR also decreased Aβ secretion [3].
Indeed, the inactivation of AMPK was linked to increased Alzheimer’s risk in obese patients with type 2 diabetes [3].
In mice with Huntington’s disease, AMPK activation promoted neuronal loss and brain decay [3]. But then again, another study showed that treatment with metformin significantly prolonged survival time in rodents with this disease [12].
Genetic activation of AMPK was also shown to protect against neuronal loss in Parkinson’s disease models in flies [3].
A Role in Cancer?
The role of AMPK in cancer is complicated and poorly understood [4].
AMPK activation can protect against DNA damage from oxidative stress. This would protect against tumor initiation [4].
It’s also anti-cancer by inhibiting mTOR [4].
On the other hand, AMPK promotes glucose/energy uptake by cells, a process which can be hijacked by tumors once they have formed [4].
Given the above, some researchers have suggested that AMPK activation is beneficial for cancer prevention, but not necessarily for cancer treatment [4].
AMPK activation by its activators (AICAR and metformin) increased UVB-induced DNA repair in normal human skin cells. Topical treatment with AICAR and metformin not only delayed the onset of UVB-induced skin tumor formation but also reduced the number of tumors in mice [16].
Potential Negatives of AMPK
AMPK can suppress PPAR alpha and PPAR gamma [17], two important proteins that regulate metabolism and gene expression.
Activating AMPK (outside of the brain)
Healthy diet and exercise are the necessary first steps to a healthy lifestyle, and they’re also the most reliable bet for weight loss. Before adopting any other strategies, talk to your doctor about the best ones for you.
Best AMPK Activators
1) Exercise
Exercise uses energy (in the form of ATP), and the resulting lack of energy stimulates AMPK [2].
AMPK is stimulated by muscle contraction. High-intensity exercise significantly increases the activity of AMPK in healthy humans [2].
Many beneficial effects of exercise are carried out through AMPK, such as the insulin-sensitizing effect [4].
2) Calorie Restriction
Calorie restriction has been associated with many beneficial effects on aging, diabetes, and cancer. Some of these effects are mediated by AMPK. It was shown that calorie restriction activates AMPK through multiple mechanisms [4].
Overeating inhibits AMPK, and AMPK activity is decreased in obese individuals [4].
High glucose levels, high levels of amino acids, especially branched-chain amino acids, and excess saturated fat inhibit AMPK. Elevated insulin also inhibits AMPK [4].
Calorie restriction stimulates adiponectin secretion from fat cells. Adiponectin activates AMPK in multiple tissues, including skeletal muscles [4].
Adiponectin secretion is significantly reduced in obese individuals, which partially explains reduced AMPK activity in these individuals [4].
3) Decrease Inflammation
AMPK can both decrease inflammation and be decreased by inflammation, so it’s important to address any underlying inflammatory conditions.
Anti-inflammatory cytokines activate AMPK, while pro-inflammatory cytokines suppress it [3].
AMPK suppression in chronic inflammation contributes to insulin resistance. Reduced AMPK activity was associated with increased inflammation in the organ fat tissue and insulin resistance in morbidly obese individuals [4].
4) Cold Exposure
In rats, exposure to cold increased AMPK activation in the hypothalamus and stimulates food intake. This effect has not been reproduced in humans [18].
5) Lipoic acid
α-Lipoic acid (ALA) may activate AMPK in muscles and other tissues, though its precise mechanism and effects have not been sufficiently investigated. Some studies have suggested that ALA may decrease hypothalamic AMPK, which could help reduce appetite and food intake [19, 13].
Natural Supplements
These supplements have not been approved by the FDA for medical use and generally lack solid clinical research. Regulations set manufacturing standards for them but don’t guarantee that they’re safe or effective. Speak with your doctor before supplementing.
That said, numerous polyphenols have been found to activate AMPK in cell and animal studies. These include:
- Resveratrol from red grapes [19, 13]
- Quercetin from many plants including fruits, vegetables, and grains [19, 13]. Note that quercetin increases AMPK in fat, liver, and muscle but inhibits hypothalamic AMPK [20].
- Genistein found in a number of plants such as soybeans [19].
- EGCG from green tea [19, 13]
- Berberine from Berberis vulgaris, Berberis asitata and Coptis chinensis [19, 13].
- Curcumin from turmeric [19, 13]
- compounds isolated from Solomon’s seal (Polygonatum odaratum) [13].
- Anthocyanins found in blueberries, bilberries, grape seed extract and pine bark extract [21].
- Apigenin [22]
- Zinc [23]
- Nicotine (in fat cells) [24, 25] and mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of nicotine [26].
- Palmitoylethanolamide (activates AMPK in fat tissue, but inhibits it in the hypothalamus) [27]
- Bitter Melon (Cucurbitane) [13]
- Carnitine [28]
- Glucosamine [29, 30]
- Extra virgin olive Oil [31]
- Fish Oil – EPA [32], DHA [33]
- Cinnamon [34]
- Astragalus [35, 36]
- Reishi [37]
- Ginseng/Ginsenosides. A number of ginsenosides have been reported to activate AMPK, resulting in an increased glucose uptake, decreased liver triglyceride and cholesterol levels, and the inhibition of fat production and liver glucose production [19].
- Apple Cider Vinegar /Acetic acid [38], Pomegranate vinegar [39]
- Rooibos [40]
- Creatine [41]
- CoQ10 [42]
- Gynostemma [43]
- Hydroxytyrosol [44]
- Baicalin [45, 46]
- Fucoidan [47]
- Danshen/Salvia Miltiorrhiza/Tanshinone IIA [48]
- Red yeast rice (monascin and ankaflavin) [49]
- Arctigenin from the seeds of burdock (Arctium lappa) [13].
- Panduratin from Chinese ginger (Boesenbergia pandurate) [13].
Hormone Pathways
These hormone pathways stimulate and regulate AMPK activation in everyday life. Maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly is the best way to keep each of these hormones in balance.
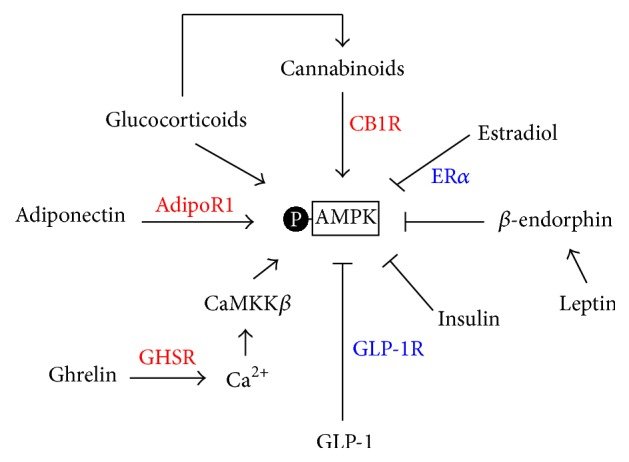
1) Adiponectin
Fat cells produce adiponectin [13], which serves as a starvation signal [2].
In fasting, adiponectin increases and stimulates AMPK, leading to the induction of food intake and reduction of energy expenditure. After refeeding, a decrease in adiponectin level is accompanied by blunted AMPK activity [2].
2) Leptin
Leptin, the satiety hormone secreted by fat cells in the presence of insulin, prevents overeating by inhibiting AMPK in the hypothalamus to suppress appetite [4]. It also activates AMPK in muscle [4].
3) Thyroid hormone T3
The thyroid hormone T3 increases cellular oxygen consumption and activates AMPK in the muscles [50].
4) Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide activates AMPK [51, 52].
Drugs
The drugs discussed here have not been approved for the purpose of activating AMPK. Do not use medications without a prescription from your doctor.
1) Metformin
Metformin is a blood-sugar-lowering agent. It is widely used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes [13].
AMPK mediates many of the antidiabetic actions of metformin: stimulation of fat burning and glucose uptake, and decreased fat production and liver glucose production [19].
2) Aspirin
Salicylate is a direct activator of AMPK [19].
Aspirin reduces circulating free fatty acids and TG levels in obese patients with type-2 diabetes and increases fat breakdown during fasting in healthy humans, which can be explained by the direct effect of aspirin on AMPK activation [4].
Hypothalamic AMPK
Activating AMPK in the brain (hypothalamus) has the opposite effect as it does when activating it in the liver, fat, and muscles. Activating AMPK in the brain increases appetite and may increase weight gain. When it’s activated in non-brain tissue, it promotes fat burning.
Inhibiting AMPK in the brain likewise reduces appetite and may cause weight loss. However, no substance or strategy has sufficient evidence to support claims of activating or inhibiting hypothalamic AMPK. The best strategy for weight loss remains diet and exercise.
Substances that Activate Hypothalamic AMPK
1) Ghrelin
Ghrelin is a hunger hormone produced in the stomach and released during fasting. Ghrelin is essential for survival during severe calorie restriction or fasting when it maintains blood glucose levels [4].
Ghrelin activates AMPK in the hypothalamus and stimulates food intake [4], however, it inhibits AMPK in the fat tissue and liver [4].
2) Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids stimulate AMPK activity in the hypothalamus leading to increased appetite [2]. However, it decreases AMPK in fat cells and liver, similar to Ghrelin [53].
3) Cortisol
Cortisol stimulates AMPK activity in the hypothalamus [2].
Substances that Inhibit Hypothalamic AMPK
Hormones
Natural Substances
- Lipoic acid [19, 13]… it increases AMPK in muscles, fat and liver cells [54, 55, 56]
- Quercetin [20]… it increases AMPK in fat, liver, and muscle [57, 58, 59]
- Nicotine [60] – Smokers around the world commonly report increased body weight after smoking cessation. Nicotine-induced weight loss is associated with the inactivation of hypothalamic AMPK [60].
- Ketones [61]

